Performance Evaluation Investigation for Conventional Solar Still with Different Additives
Keywords:
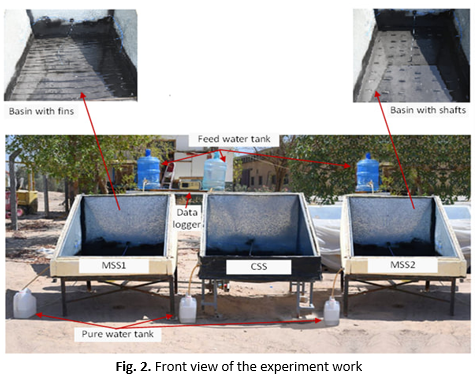
Fresh Water, Exergy analysis, CSS- Shafts, CSS-Fins, Solar StillAbstract
The demand for freshwater is on the rise due to a multitude of human activities and a rapidly expanding global population. The yielding of pure water heavily depends on the utilization of traditional sources of energy, which in turn contributes to environmental contamination. Consequently, there is a necessity to explore alternative options, such as clean energy (specifically solar energy). Numerous systems for desalination have been devised to confront this inadequacy. One such system is the conventional solar still (CSS), which is easy to production, operate and continue, but the limited production has prompted researchers to consider various improvements to increase the productivity of the still. This study elucidates a sustainable way to diminishing the duration required for the evaporation process, thereby augmenting the efficiency of clean water solar energy production. All investigates were operated under the local weather circumstances of Najaf city, central-western Iraq. The peak time for the experimental work is 14:00 PM. The Everyday output of the CSS, MSS1 and MSS2 is 2.225, 2.860 and 3.939 L/m2.day, respectively. The outcomes displayed that the maximum value of the thermal efficiency and the exergy efficiency were obtained estimated at 29.34% and 3.96% for CSS, 40.1% and 4.85% for MSS1 and 59.45% and 6.75% for MSS2. While the cost of 1 litter of pure water improved by 14.67% for MSS1 and 40.02% for MSS2 as compared with that from CSS